APP Security
18.Aug.2020
Mobile APPs are booming, but are the APPs you use really safe?
With the development of technology and network transmission, mobile applications are increasingly popular. Many APPs have sprung up to bring people a high degree of convenience. Eating, clothing, housing, transportation, education and entertainment can be done through APPs. Since APPs have become an indispensable part of life, they have also become one of the channels for people with bad intentions to steal information. Almost everyone has such experience that when you download and use the APP, it will often pop up the page asking you to authorize the use of the cell-phone such as the address book, making calls, microphone, GPS positioning, etc. Most users may easily ignore the relevance of APPs permission request, allowing malicious APPs to obtain unnecessary system permissions and resulting in the leakage of a lot of important information. Previously, there was a malicious auto-beautification APP requesting permission to access the mobile phone text messages. Through authorization, it can obtain the SMS verification code sent to the mobile phone, and further activate the payment mechanism to steal the user's money. In addition to requesting unnecessary system permissions, APPs has other security vulnerabilities, which can cause user data leakage. The following will explain the common APP vulnerabilities.
According to the common mobile device risk report published by the Open Web Application Security Project (OWASP), the security problems of most APPs are superfluous functional modules, insecure data storage and insecure transmission. These risks would not pose immediate hazards. However, the attack techniques of hackers are increasingly sophisticated and changeable. Once an unused module is found and utilized, it would not only be a breach for hackers causing data leakage or malicious data tampering, but also might cause a chain reaction of adverse effects on the internal system of the enterprise. For example, "USB Debugging" is a way to communicate with the Android Software Development Kit (SDK) over a USB connection. It allows users, through a personal computer, to control Android devices and transfer files, while getting the operation information of the system and APP, such as log files and configuration files. In the past, there were malwares that infected Android devices via USB. "USB debugging" is a double-edged sword, which can not only obtain system information, but also allow mobile devices to be easily controlled. Therefore, it is recommended to turn off this function normally.
According to the common mobile device risk report published by the Open Web Application Security Project (OWASP), the security problems of most APPs are superfluous functional modules, insecure data storage and insecure transmission. These risks would not pose immediate hazards. However, the attack techniques of hackers are increasingly sophisticated and changeable. Once an unused module is found and utilized, it would not only be a breach for hackers causing data leakage or malicious data tampering, but also might cause a chain reaction of adverse effects on the internal system of the enterprise. For example, "USB Debugging" is a way to communicate with the Android Software Development Kit (SDK) over a USB connection. It allows users, through a personal computer, to control Android devices and transfer files, while getting the operation information of the system and APP, such as log files and configuration files. In the past, there were malwares that infected Android devices via USB. "USB debugging" is a double-edged sword, which can not only obtain system information, but also allow mobile devices to be easily controlled. Therefore, it is recommended to turn off this function normally.
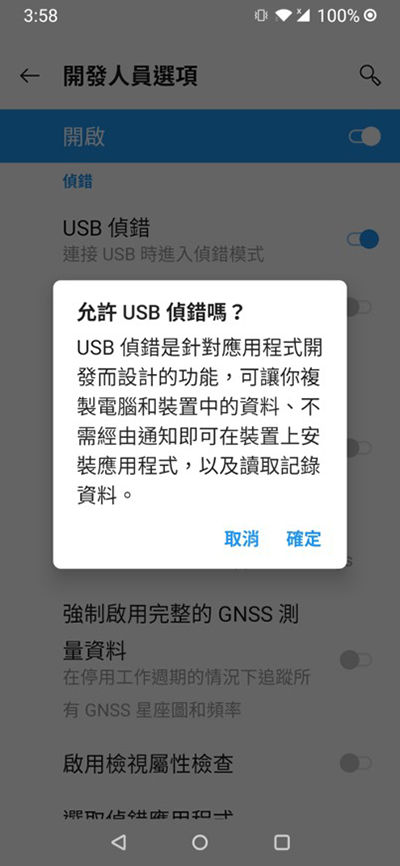
USB debugging mode
Confidential and sensitive data need to be encrypted when storing or transferring
By analyzing the past accumulated APP test results, the easiest thing for developers to overlook is to store confidential and sensitive data in plaintext form. According to the APP testing standards of Taiwan's Industrial Development Bureau (IDB), the contents of the APPs stored on mobile devices (including configuration files, database files, temporary files, log files and other sensitive data) shall not be stored in plaintext form and must be encrypted so as to protect personal privacy. Therefore, if the APP does not encrypt sensitive data during storage or transmission, or if the APP directly stores the data in an insecure storage location by plaintext form, other arbitrary and unauthorized APPs may access the data, causing personal privacy leakage.
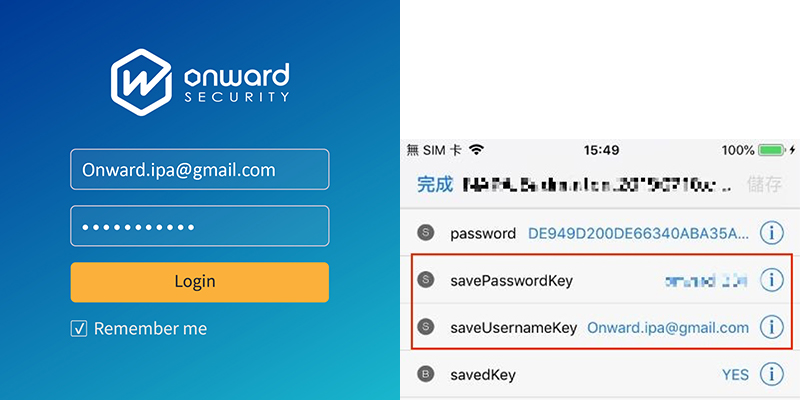
Store confidential and sensitive data in plaintext form
Failure to properly check certificates can leak important information
Most APPs need to communicate with the server through a network connection. If the information security protection during the connection process is neglected and APPs did not check whether they are connected to the correct server, attackers can use Man-in-the-Middle Attack (MITM) to tamper with messages, steal data and plant malicious programs. Therefore, developers must pay attention to checking the correctness of the certificate during the development process. When the certificate expires or the information of the issuing unit is incorrect, the connection must be immediately terminated to avoid leakage of important data. The following figure is an example. Attackers obtain the user login account and password from the APP, because it does not check the connection security.
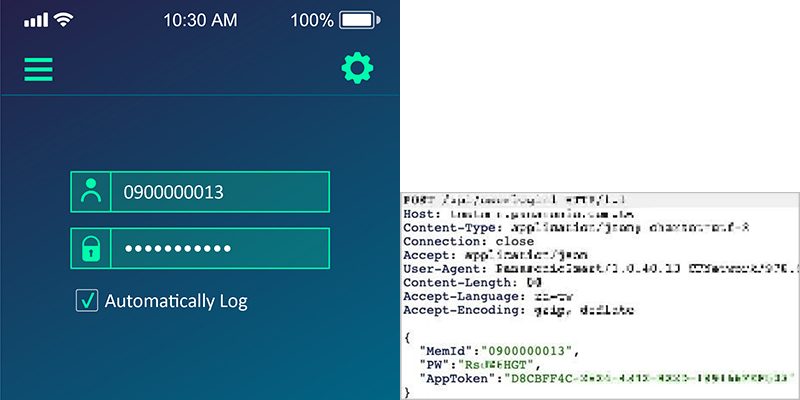
Schematic diagram of MITM - intercepting sensitive user information
Information security solution for mobile APPs
Regarding the APP security issues faced by enterprises, Onward Security has obtained Taiwan's official recognition for mobile APP basic information security testing standards in 2016. Since then, its qualified laboratory has accumulated more than 500 APPs testing experience. Its customers include government, finance, telecommunication, high-tech, Internet of Things, aviation and online shopping. Besides, Onward Security can also provide testing services in accordance with the international mobile APP guidelines - OWASP Mobile Security Testing Guide. With source code scanning, vulnerability scanning, penetration testing, information security consulting, education and training and other professional security services, it offers vendor structure enhancement, information security testing and consulting services. Through the one-stop APP security development services, Onward Security is capable of helping customers comprehensively improve Cloud services and APP security.

References:
[1] TREND MICRO Security Intelligence Blog,< Fake Photo Beautification APPs on Google Play can Read SMS Verification Code to Trigger Wireless Application Protocol (WAP)/Carrier Billing>,2019.10.。
https://blog.trendmicro.com/trendlabs-security-intelligence/fake-photo-beautification-APPs-on-google-play-can-read-sms-verification-code-to-trigger-wireless-APPlication-protocol-wap-carrier-billing/
[2] iThome,〈遺留無用功能或檔案而疏於防護〉,2019.04。
https://www.ithome.com.tw/news/130259.
[3] 商業周刊,〈導入APP資安檢測〉,2019.07。閱於2020.06.29。
https://www.businessweekly.com.tw/focus/indep/38870.
[4] 經濟部工業局,〈行動應用APP安全開發指引v1.2〉,2019.06。
[5] OWASP,“OWASP Mobile Top 10 2016”,2016.03。
https://owasp.org/www-project-mobile-top-10